
Social Darwinism, as a direction,was formed in the 19th century. The works of the founders of the teaching had a colossal influence on contemporaries. Naturally, Darwin's law itself, being a large-scale scientific event, could not help but touch upon the field of social knowledge. In England, Spencer and Bedzhgot systematically applied the teaching to real life. The latter, being a publicist, an economist, tried to use the principles on which the direction in question was based while studying historical processes in society. And by the end of the 19th century Spencer's ideas were assimilated by leading figures Giddings and Ward.
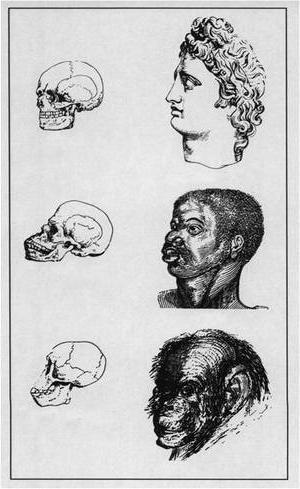
Social Darwinism. Key Concepts
For the entire social science of the 19th century, and infeatures of its second half, has become a characteristic series of priority moments. Darwin himself highlighted these key concepts. The theory followed by scientists after him became a kind of paradigm that penetrated various areas of social thought. These basic concepts were "natural selection", "survival of the strongest," "struggle for existence." In this regard, social Darwinism has not only acted as a special direction.
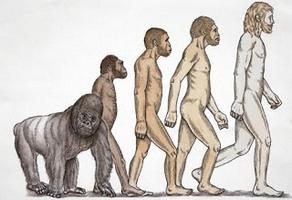
Social Darwinism at the end of the 19th century

By the end of the nineteenth century, ideas"Natural selection" went beyond the scope of the scientific sphere and became very popular in business, publicism, mass consciousness, fiction. Representatives of, for example, the economic elite, business tycoons, based on the theory of evolution, concluded that they are not only lucky and talented, but also considered a visible embodiment of victory in the struggle for existence in their particular sphere. In this regard, it is erroneous, according to the researchers, to regard social Darwinism as a doctrine based only on biological aspects and being a simple continuation of them. It can be defined as a direction that reduces the laws of social development to the principles of natural evolution. Social Darwinism, in particular, considers the struggle for survival as a defining aspect of life. At the same time, the non-biological principles of the doctrine indicate that, in a sense, the old social thought is actualized and grounded. Among all the signs of the direction under consideration, one of the main points is the consideration of life as an arena, on which there is a universal and continuous struggle, conflicts, clashes between individuals, societies, groups, customs, institutions, cultural and social types.
</ p>